Nvidia has just announced a new supercomputer that may change the future of AI. The DGX GH200, equipped with nearly 500 times more memory than the systems we’re familiar with now, will soon fall into the hands of Google, Meta, and Microsoft.
The goal? Revolutionizing generative AI , recommender systems, and data processing on a scale we’ve never seen before. Are language models like GPT going to benefit, and what will that mean for regular users?
Describing Nvidia’s DGX GH200 requires the use of terms most users never have to deal with. “Exaflop,” for example, because the supercomputer provides 1 exaflop of performance and 144 terabytes of shared memory. Nvidia notes that this means nearly 500 times more memory than in a single Nvidia DGX A100 system.
Let’s circle back to the 1 exaflop figure and break it down a little. One exaflop equals a quintillion floating-point operations per second (FLOPs). For comparison, Nvidia’s RTX 4090 can hit around 100 teraflops (TFLOPs) when overclocked. A TFLOP equals one trillion floating-point operations per second. The difference is staggering, but of course, the RTX 4090 is not a data center GPU. The DGX GH200, on the other hand, integrates a substantial number of these high-performance GPUs that don’t belong anywhere near a consumer PC.
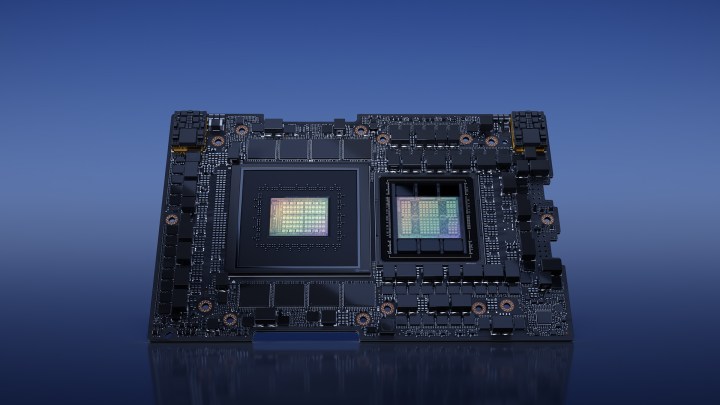

The computer is powered by Nvidia’s GH200 Grace Hopper superchips. There are 256 of them in total, which, thanks to Nvidia’s NVLink interconnect technology, are all able to work together as a unified system, essentially creating one massive GPU.
The GH200 superchips used here also don’t need a traditional PCIe connection between the CPU and the GPU. Nvidia says that they’re already equipped with an ARM-based Nvidia Grace CP,U as well as an H100 Tensor Core GPU. Nvidia’s got some fancy chip interconnects going on here too, this time using the NVLink-C2C. As a result, the bandwidth between the processor and the graphics card is said to be significantly improved (up to 7 times) and more power-efficient (up to 5 times).
Packing over 200 of these chips into a single powerhouse of a supercomputer is impressive enough, but it gets even better when you consider that, previously, only eight GPUs could be joined with NVLink at a time. A leap from eight to 256 chips certainly gives Nvidia some bragging rights.
It’s hard not to imagine that the DGX GH200 could power improvements in Bard, ChatGPT, and Bing Chat.
Now, where will the DGX GH200 end up and what can it offer to the world? Nvidia’s building its own Helios Supercomputer as a means of advancing its AI research and development. It will encompass four DGX GH200 systems, all interconnected with Nvidia’s Quantum-2 InfiniBand. It expects it to come online by the end of the year.
Nvidia is also sharing its new development with the world, starting with Google Cloud, Meta, and Microsoft. The purpose is much the same — exploring generative AI workloads.
When it comes to Google and Microsoft, it’s hard not to imagine that the DGX GH200 could power improvements in Bard , ChatGPT , and Bing Chat .

The significant computational power provided by a single DGX GH200 system makes it well-suited to advancing the training of sophisticated language models. It’s hard to say what exactly that could mean without comment from one of the interested parties, but we can speculate a little.
More power means larger models, meaning more nuanced and accurate text and a wider range of data for them to be trained on. We might see better cultural understanding, more knowledge of context, and greater coherency. Specialized AI chatbots could also begin popping up, further replacing humans in fields such as technology.
Should we be concerned about potential job displacement, or should we be excited about the advancements these supercomputers could bring? The answer is not straightforward. One thing is for sure — Nvidia’s DGX GH200 might shake things up in the world of AI, and Nvidia has just furthered its AI lead over AMD yet again .



